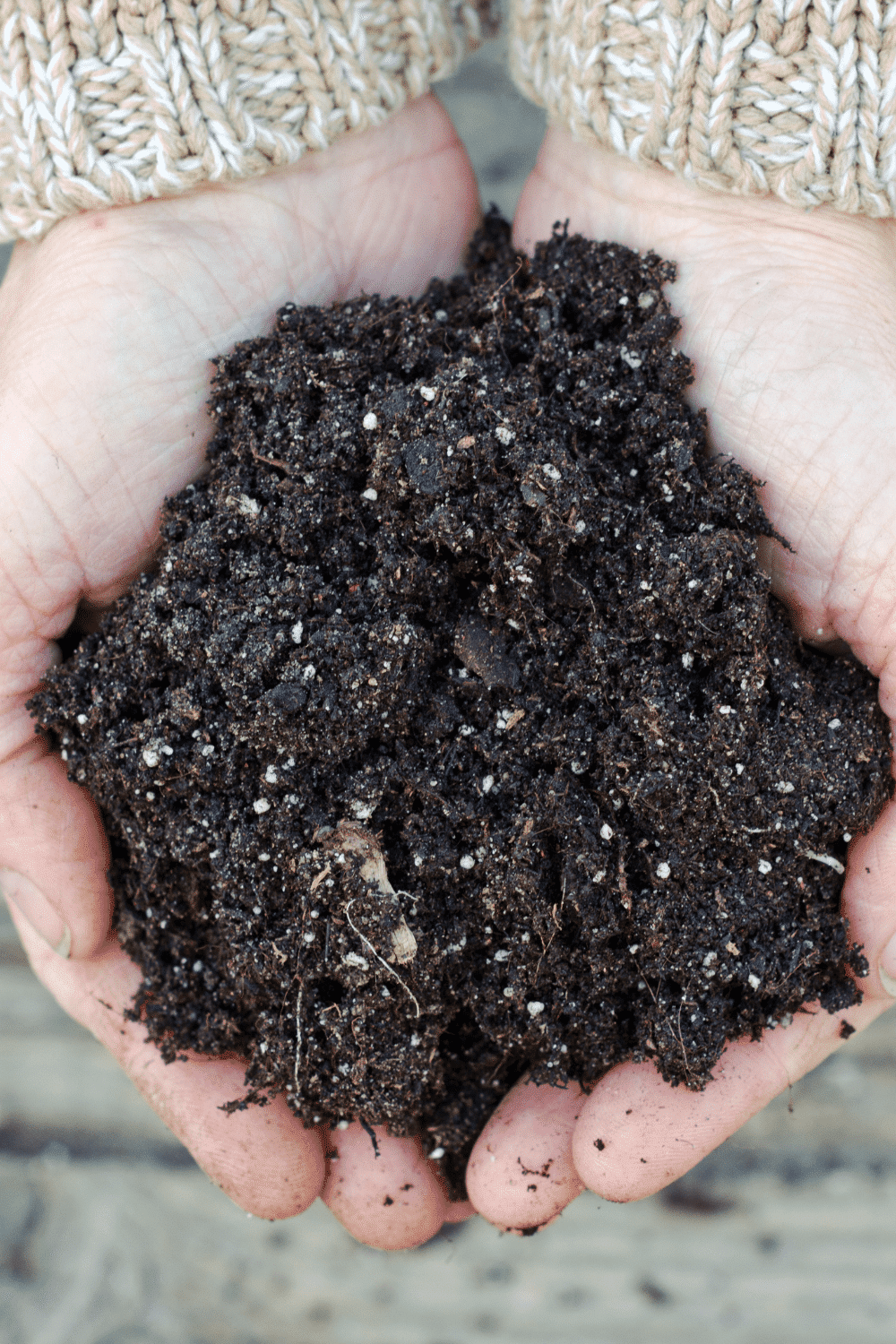
Have you ever seen small little grains of what looks like white styrofoam in your soil mix? It may look like something you don’t want in your garden, but it is actually perlite. Perlite is a type of volcanic glass that is commonly used as a soil amendment in gardening. It is formed from obsidian, a volcanic rock that is heated to high temperatures to create small, lightweight, and porous particles. Since the white rocks, which come in various grain levels, are amorous, they retain moisture well in soil mixes. Since perlite is sterile, it doesn’t add any unwanted things to your soil.
In this post, we will explain what perlite is and how to use it in your garden. We will also talk about whether perlite is a sustainable amendment in our garden and other alternatives.

What is perlite?
Perlite is naturally occurring amorphous volcanic glass with a relatively high water content, typically formed by obsidian hydration. It has the ability to expand and absorb water easily to help create aeration and space in the soil and retain water for plants. Perlite is sterile and pH-neutral, which makes it a safe and effective soil additive for promoting healthy plant growth. We use it in our garden in our raised beds to aerate the soil for effective root development and to help lower the amount of water needed since we have sandy topsoil under our raised beds.
Why use perlite in your garden?
Many gardeners love using perlite in their gardens because it lowers the amount of water that is needed in their gardens. They will use it to retain moisture naturally. This is particularly helpful for sandy soils that struggle to retain water. Mixing it into well-draining soils can be helpful when growing your vegetable garden in beds that are located in the ground. If you have more compact and clay soil that struggle with drainage, adding perlite into your compost and sand mixture could also aid in more consistent drainage in your soil.
How to use perlite in your garden?
Perlite can be used in several ways in the garden to improve soil quality and promote healthy plant growth. Here are some ways you can use perlite in your garden:
- Mix perlite into the soil: Perlite can be added to the soil to create better structure, drainage, and aeration. Mix in 10-20% perlite with soil to create a lightweight and well-draining soil mixture for almost any plant.
- Create a perlite layer for drainage: A layer of perlite at the bottom of plant pots or garden beds can improve drainage and prevent waterlogged soil, which can lead to root rot. Though you can also use rocks, if you have any leftover perlite, this is another great use. Add a layer of perlite at the bottom of the pot to give space for the water to drain properly.
- Use perlite as a growing medium: Because perlite is a lightweight, pH-neutral substrate that can support plant growth without the need for soil, it can be a great way to grow plants in a soil-less way. This is best for cactuses and plants that don’t need nutrients.
- Start seedlings in perlite: Since perlite is sterile, it is a great place to germinate your seedlings before transferring them to a large pot with soil. Just wet the medium before planting seeds.
Remember, since perlite is dusty and has fine granules, it’s important to wear gloves and a mask to avoid inhaling any fine particles. The dust can cause irritation to the skin and respiratory system if not handled carefully.
Is perlite a sustainable material?
As with anything we use in the garden, this question is important. What’s the point of growing something if it isn’t being done with the environment in mind?
Perlite’s sustainability isn’t a clear answer. Since perlite is non-renewable, meaning it doesn’t easily renew itself, but at this time, we have mined far less than what is left, there is a finite usage to it, which is important to understand. The process of mining doesn’t involve any chemicals, but it is mined and heated for it to pop into the soil with the water. The important thing is that perlite doesn’t degrade, so its need in our garden isn’t something to use year after year. Though the impact is low compared to other soil amendments, it is still important to understand that impact does exist.

What are alternatives to perlite?
Several options can offer similar benefits if you’re looking for alternatives to perlite as a soil amendment or growing medium. Here are some of the most commonly used alternatives to perlite:
- Vermiculite: Like perlite, vermiculite is a lightweight and porous material that improves soil drainage and aeration. It is made from mica minerals that are heated to high temperatures, causing them to expand and become lightweight. Vermiculite is also pH-neutral and sterile, making it a safe and effective soil amendment. Though it has the same sustainability as perlite would because it is similar in methods for extraction and sourcing.
- Coconut coir: Coconut coir is a byproduct of coconut processing that is becoming increasingly popular as a soil amendment. It is lightweight, pH-neutral, and has good water retention and drainage properties. Coconut coir is also a sustainable alternative to peat moss, which is often used as a soil amendment but is not environmentally friendly due to peat bogs being destroyed.
- Compost: Compost is a nutrient-rich material that is made from decomposed organic matter such as leaves, grass clippings, and food scraps. It can be added to soil to improve its structure, fertility, and water retention. Compost also provides a range of beneficial microorganisms that can help promote healthy plant growth.
- Rice hulls: Rice hulls are the outer covering of rice grains and are a byproduct of rice processing. They are lightweight, porous, and pH-neutral, making them a good alternative to perlite. Rice hulls also have good water retention properties and break down slowly in the soil, providing long-term benefits to plant growth.
- Sand: Sand can be used to improve soil drainage and aeration, especially in heavy clay soils. It is an inexpensive and widely available alternative to perlite, but it does not offer the same level of porosity as perlite or other lightweight materials.
Overall, there are many alternatives to perlite that can offer similar benefits depending on the specific needs of your garden. It’s always a good idea to research the properties of different materials and choose the one that best suits your growing conditions and preferences.

In conclusion, perlite is a great material to use in your garden if you consistently struggle to retain moisture in your beds. For gardeners with clay soils, it can be helpful to open and aerate the soil to allow for drainage to happen more effectively. Perlite is a sustainable product because of how it is harvested, and we do not need to replace it very often. Though there are alternatives, it may not be necessary to consider them if you aren’t adding them very often to your garden to retain moisture.
To learn more about soil and gardening, join our community and check out our Beginner Gardener Course.