Gardeners have long used Peat Moss as an amendment in potting soils (these were our top picks for potting soil) to help with moisture retention, but recent studies have confirmed that Peat Moss is an unsustainable product, and gardeners need to be seeking alternatives. In this post, we will identify what peat moss is and why it isn’t an option for those looking to be sustainable gardeners. We will also share peat moss alternatives for gardeners who want to be eco-friendly to consider when purchasing or amending their soil.

What is Peat Moss
Peat moss, or sphagnum moss, is decomposed plant material that forms in wetland environments. It has high water retention, acidity, and fibrous texture. Used as a soil amendment, like perlite, improves soil structure and moisture levels. It is used most often in potting soils and raised bed soil mixes to help create better moisture levels. However, its extraction from peatlands raises environmental concerns such as carbon emissions and biodiversity loss. Exploring sustainable alternatives is essential for minimizing its ecological impact while supporting gardening needs.
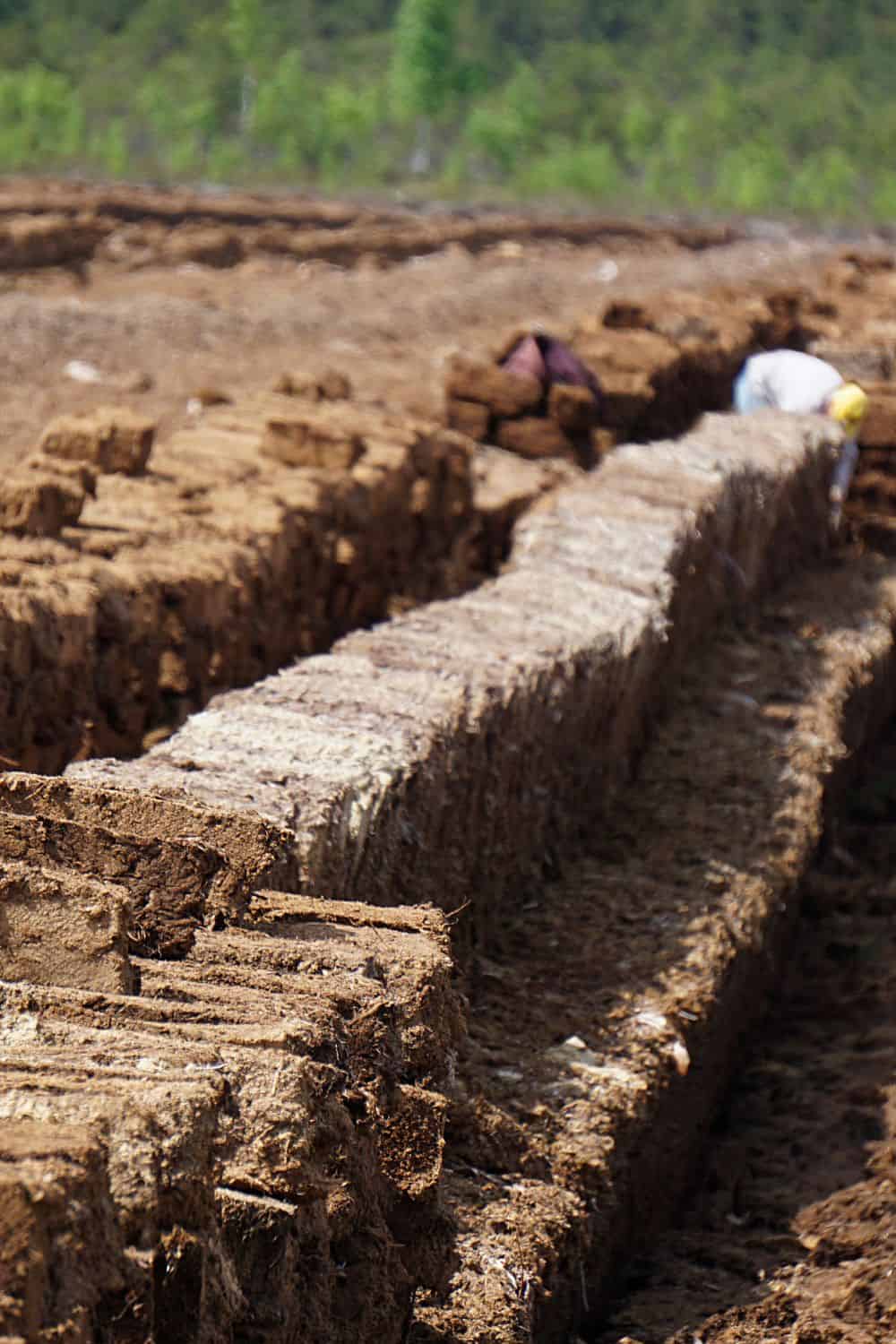

How is Peat Moss Used in the Garden
Peat moss is a versatile material with several practical applications in gardening. Here are some common uses:
- Soil Amendment: Peat moss is often added to garden soil to improve its structure and texture. Its fibrous nature helps loosen compacted soil, allowing for better root penetration and drainage.
- Seed Starting: Peat moss is an excellent medium for starting seeds. It provides a sterile and moisture-retentive environment that promotes successful germination. Its fine texture also allows for good seed-to-soil contact.
- Container Gardening: Peat moss is widely used in container gardening. It helps retain moisture in pots, preventing them from drying out too quickly. Its lightweight nature also reduces the overall weight of containers.
- Acid-Loving Plants: Peat moss has natural acidity, making it suitable for plants that prefer acidic soil conditions, such as azaleas, rhododendrons, and blueberries. It can be mixed into the soil or used as a top dressing around these plants.
- Mulching: Peat moss can be used as a mulch to suppress weed growth and conserve soil moisture. It forms a protective layer over the soil, preventing weed seeds from germinating and reducing water evaporation.
When using peat moss in the garden, it is essential to consider its environmental impact. Gardeners can explore sustainable options such as compost, coconut coir, or leaf mold as an alternative or supplement. These alternatives offer similar benefits while minimizing the ecological footprint associated with peat moss extraction.

Understanding Peat Moss’s Environmental Impact
Peat moss extraction and usage have significant environmental implications that need to be understood. Here are the key aspects of its impact:
- Carbon Emissions: Peatlands, where peat moss forms, act as crucial carbon sinks, storing vast amounts of carbon dioxide. However, when peat moss is extracted from these peatlands, it releases carbon into the atmosphere. The draining and drying of peatlands during extraction cause the decomposition of organic matter, releasing stored carbon as carbon dioxide, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and climate change.
- Habitat Destruction: Peatlands are unique and fragile ecosystems that provide habitats for a wide range of plant and animal species. The extraction of peat moss involves draining and degrading these ecosystems, leading to the destruction of habitat for specialized flora and fauna. This loss of biodiversity can have long-lasting ecological consequences.
- Water Loss and Soil Degradation: The drainage of peatlands for peat moss extraction disrupts the natural water-holding capacity of these wetland ecosystems. This alteration affects water availability and can lead to changes in hydrological patterns, potentially impacting nearby water bodies, such as rivers and lakes. The degradation of peatland soils due to extraction practices further exacerbates these environmental issues.
- Loss of Ecosystem Services: Peatlands provide important ecosystem services, such as water purification, flood control, and maintenance of water tables. Peat moss extraction disrupts these services, potentially compromising water quality, exacerbating flooding risks, and affecting the hydrological balance in surrounding areas.
Considering the environmental impact of peat moss, it is crucial to explore alternative gardening practices that reduce or eliminate its usage. Sustainable options like compost, coconut coir, and leaf mold can provide similar benefits while minimizing the negative ecological footprint associated with peat moss. We can preserve valuable ecosystems and mitigate climate change impacts by adopting these alternatives and promoting responsible peatland conservation.
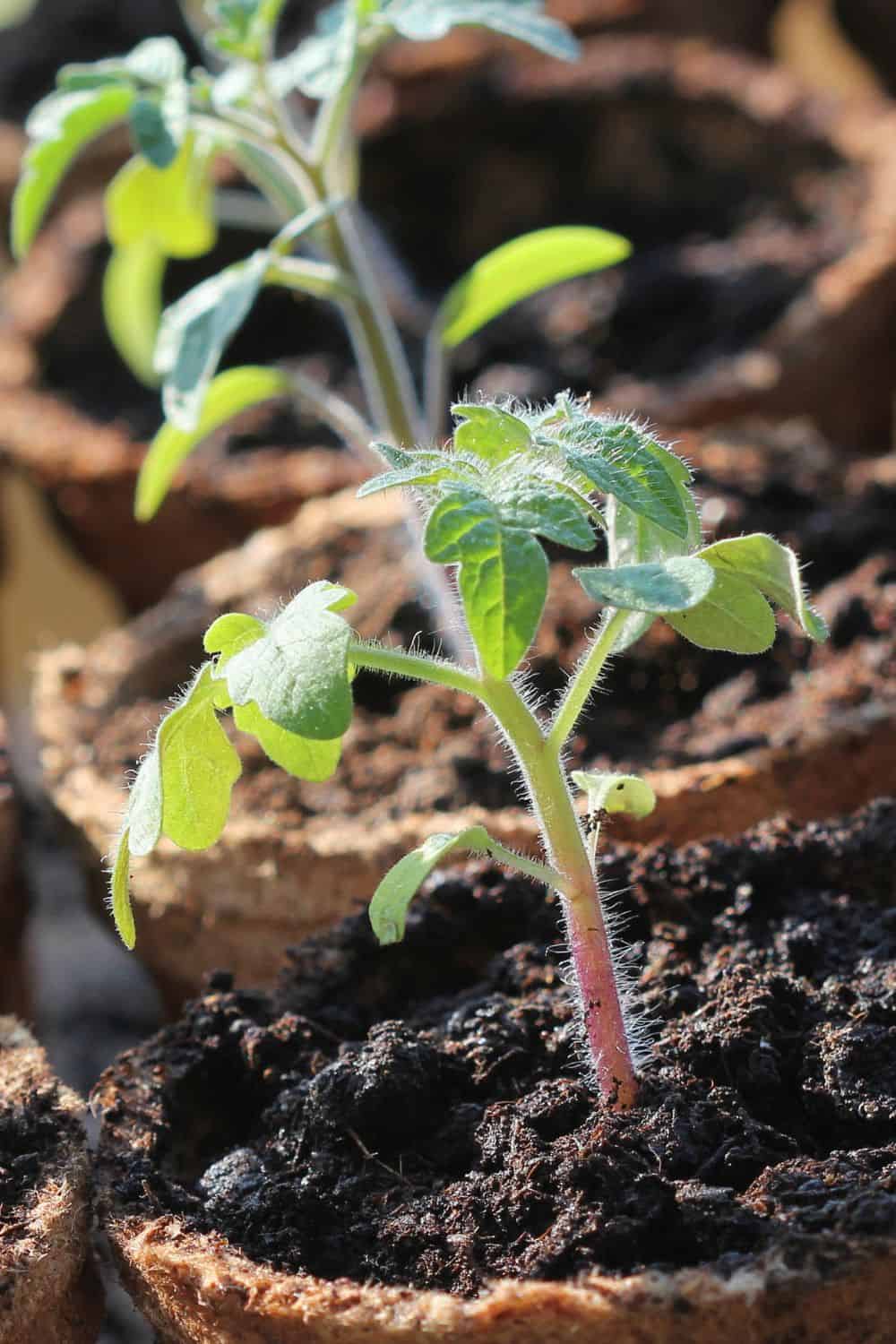

Environmentally Sustainable Alternatives to Peat Moss in the Home Garden
While peat moss has been a popular choice for gardeners, several environmentally sustainable alternatives are available. Here are some alternatives to consider:
- Coconut Coir: Coconut coir, derived from coconut husks, is an excellent substitute. It has similar water retention capabilities and improves soil structure. Coconut coir is a renewable resource and is often produced as a byproduct of the coconut industry.
- Compost: Using compost as a soil amendment provides numerous benefits. It enriches the soil with organic matter, improves nutrient availability, and enhances soil structure. Compost can be created from kitchen scraps, yard waste, and other organic materials, making it an eco-friendly choice. Though compost is a great option, buying the right one is even more important. I always suggest looking local first. Making your own is also best. Compost can sometimes use peat moss, so look and read labels. You can read more in our Soil Course right here.
- Leaf Mold: Leaf mold is the result of the decomposition of autumn leaves. It enhances soil fertility, retains moisture, and improves soil structure. Leaf mold can be made by collecting fallen leaves and allowing them to decompose over time.
- Peat-free Potting Mixes: Many commercial potting mixes now offer peat-free alternatives. These mixes incorporate various organic materials, such as compost, coir, bark, and wood fiber. They provide similar benefits to peat-based mixes.
- Wood bi-products: These products would be things like sawdust or wood shreds from mixed hardwoods. These are typically arborist or woodworker bioproducts, but they make great garden options to retain moisture just as peat does.
When considering alternatives, it is essential to assess their suitability for specific plants and gardening needs. Experimenting with different options and finding the right combination for your garden can lead to sustainable and thriving plant growth. By transitioning away from peat moss and embracing eco-friendly alternatives, we can cultivate healthy gardens while preserving our precious ecosystems.
Benefits of Peat Moss Alternatives
Exploring alternatives to peat moss in gardening offers several environmental and plant health benefits. Here are the advantages of using sustainable alternatives:
- Reduced Carbon Footprint: Peat moss alternatives, such as coconut coir, compost, and leaf mold, contribute to lower carbon emissions. By choosing these options, gardeners help minimize the release of stored carbon into the atmosphere, mitigating the impact of climate change.
- Enhanced Soil Structure: Sustainable alternatives improve soil structure by promoting better aeration and water drainage. Coconut coir and compost, for example, have excellent water retention properties while preventing soil compaction. They create a favorable environment for root growth and nutrient absorption.
- Improved Moisture Retention: Alternatives like coconut coir and compost retain moisture effectively, reducing the frequency of watering. This property is especially beneficial in dry climates or for plants that require consistent moisture levels.
- Nutrient Availability: Compost and organic alternatives enrich the soil with essential nutrients. They provide a natural source of plant nutrients, fostering healthier growth and reducing reliance on synthetic fertilizers.
- Support for Beneficial Soil Microorganisms: Peat moss alternatives contribute to the development of a robust and diverse soil microbiome. The organic matter in compost and leaf mold serves as a food source for beneficial soil organisms, fostering a balanced ecosystem underground.
- Environmental Conservation: Choosing peat moss alternatives helps preserve peatlands, delicate ecosystems that provide numerous ecological benefits. By reducing peat moss extraction, gardeners contribute to the conservation of these unique habitats, protecting biodiversity and maintaining crucial ecosystem services.
By embracing sustainable alternatives to peat moss, gardeners can create thriving gardens while actively supporting environmental stewardship. These alternatives offer a range of benefits that promote healthy plant growth, reduce environmental impact, and contribute to a greener future.
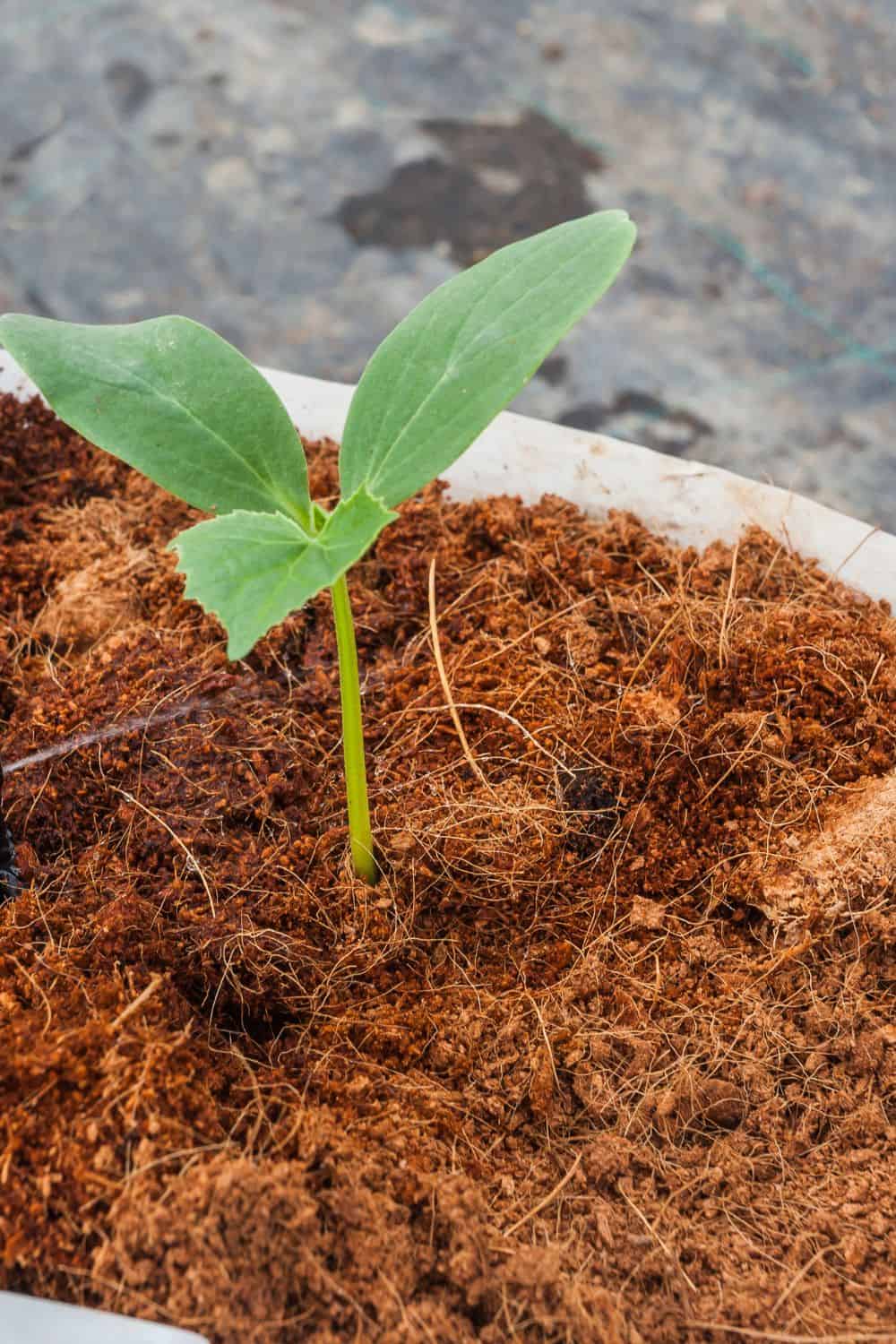

How to Use Alternatives in the Home Garden
Sustainable alternatives to peat moss can be effectively used in various gardening practices. Here’s how they can be applied in the garden:
- Soil Amendment: Similar to peat moss, alternatives like coconut coir, compost, and leaf mold can be incorporated into garden soil. Mix them thoroughly with the existing soil to improve its structure, water retention, and nutrient content. Aim for a balanced ratio based on the specific requirements of your plants.
- Seed Starting and Transplanting: Peat moss alternatives are ideal for starting seeds and transplanting seedlings. Use coconut coir or a mixture of compost and vermiculite as a seed-starting medium. Their moisture retention and nutrient-rich properties create a favorable environment for successful germination and initial growth.
- Container Gardening: Peat moss alternatives are well-suited for container gardening. Fill containers with a blend of coconut coir, compost, and perlite or vermiculite. This combination provides excellent drainage, moisture retention, and nutrient availability, supporting healthy root development in potted plants.
- Mulching: Apply compost or leaf mold as a natural mulch around garden beds, containers, and plantings. Spread a layer of about 2-3 inches around the base of plants, ensuring it doesn’t touch the stems. Mulching helps retain soil moisture, suppresses weeds, and promotes a more favorable microclimate for plant roots.
- Soil Improvement: When faced with challenging soil conditions, such as heavy clay or sandy soils, incorporate compost or coconut coir to enhance soil fertility and structure. Work these alternatives into the soil during bed preparation or as top dressings for existing plantings.
- Amending Potting Mixes: Commercial potting mixes often contain peat moss. Opt for peat-free mixes that utilize coconut coir, compost, or other organic materials. If using a pre-packaged mix, supplement it with additional compost or coconut coir to enhance its water retention and nutrient content.
Remember to assess the specific needs of your plants and make adjustments accordingly when using peat moss alternatives. Experimentation and observation will help you determine your garden’s ideal combination and application methods, ensuring optimal plant growth while reducing environmental impact.
Peat moss has been used for a long time in gardening, but it has recently begun being banned for its environmental impacts. Many amazing alternatives have just as great benefits in your garden and lower impact on the environment as well. Using peat moss in your garden isn’t necessary, but it is important to understand what it is.
Learn more about soil by taking our Soil Basics course. You will learn everything you need to know about soil and amending it properly. As a bonus, you receive a 3-month membership to our online community as well for taking the course.